
Cloud Computing Services: Examples, Applications, and Architecture
How Cloud Computing Services Work in Real-World Systems
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses store and manage data, run apps and scale their operations. Organizations no longer have to depend solely on local or physical systems and can have access to compute resources online. This shift has enabled organizations to save costs, gain flexibility of operations and have greater agility to respond with changes in business needs. Cloud computing is a means of gaining access to servers, storage, processing power and software without having to physically own or maintain it.Cloud providers manage and deliver these services through secure data centres, making them more accessible for businesses of any size. This article will examine cloud computing services and real-world examples. We’ll also look at practical cloud applications and the architecture and infrastructure behind cloud technology. Many modern AI-based platforms rely on cloud computing services to process large workloads efficiently.

What Are Cloud Computing Services
The transfer of technological resources via the Internet is known as cloud computing. Cloud computing allows businesses to use computing power, databases, and applications without installing or managing hardware. Businesses just pay for the servers and licenses they use, rather than buying them all at once.This model enables faster deployments and lower upfront costs, as well as easier scalability.
Core Characteristics of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud services typically offer:
- On-demand access to computing resources
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Remote accessibility from any location
- Automatic updates and maintenance
- High availability and reliability
These characteristics make cloud solutions attractive for startups, enterprises, and growing organizations alike.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
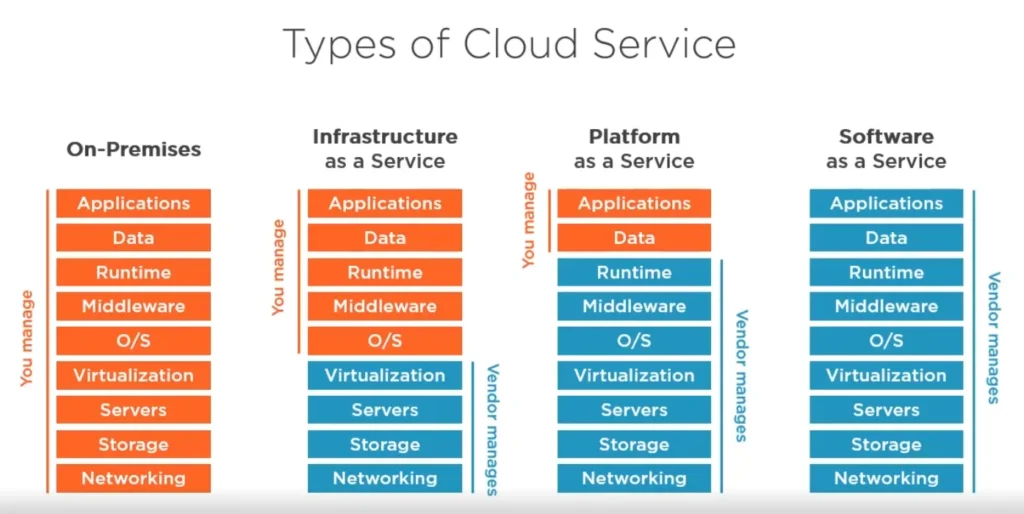
1. Software as a Service
Software as a Service allows access to applications using a web browser without downloading. All users have to do is log in and get to work. Familiar SaaS products are applications for email, collaboration and customer relationship management platform. It’s a model that eliminates software maintenance and makes certain that users always use the most recent version.
2. Platform as a Service
Platform as a Service provides developers with the tools they need to create, test, and launch apps.It saves you the hassle of maintaining servers, OSs or runtimes. PaaS is one of the most common use cases for application development and testing, because it keeps teams focused on their code instead of infrastructure.
3. Infrastructure as a Service
Businesses can purchase servers, storage, and networking as a service through Infrastructure as a Service.These companies get to control their systems without having to pay for things like physical hardware. This is popular among firms dealing with custom applications or sophisticated workloads.
Cloud Computing Examples and cloud computing applications in Real Life
Real-world examples make it easier to understand what cloud computing is all about.
1.Business and Enterprise Use
Organizations large and small use cloud services to host websites, handle their internal systems and store company data. Business cloud computing – It enables businesses to continue supporting remote workforces, processing big data, and scaling operations without having to deal with the restraints of an on-premises environment.
2.Everyday Applications
Cloud storage services, streaming programs (like Netflix or Pandora), and some web-based solutions like Google Docs are all good examples of cloud computing. These are cloud-based services designed to get your content to you in the most reliable manner no matter what device you’re using.
3.Education and Collaboration
Cloud-based platforms are widely adopted in academia to deliver e-classrooms, share resources such as lectures and assignments and store the student data safely.
Enterprise Cloud Computing Explained
Enterprise cloud computing addresses the performance, security and compliance requirements of business customers. Enterprises typically rely on private and public cloud environments for flexibility with control.
This new strategy provides a way to secure sensitive data and leverage the scalability of cloud.
Cloud Computing Infrastructure Fundamentals
Cloud computing infrastructure represents the physical and virtual resources that form the cloud services.
These components typically include:
- Data centers
- Physical servers
- Networking equipment
- Virtual machines
- Storage system
This infrastructure is designed to operate continuously with redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure uptime.
Why Infrastructure Matters
Durable infrastructure provides for ongoing performance and availability. Organizations rely on this framework for the uninterrupted delivery of services.
Cloud Computing Architecture Overview
Cloud architecture: how cloud components are networked together. This encompasses client-side apps, server-side systems, databases and network connections.

Good architecture assures scalability, security and makes most of the resources.
Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Cloud services are built on top of virtualization technology. It allows a physical machine to be divided into several virtual machines. This is efficient use of resources and rapid deployment of applications. Isolation also provides a level of support for security and stability. Virtualized environments are also widely used to support AI image generation systems that require high processing power.
Benefits of Using Cloud Computing Services
Practical reasons to use cloud for businesses:
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Faster deployment of applications
- Easy scalability during growth
- Improved collaboration and remote access
- Automatic updates and maintenance
These benefits help organizations remain competitive in fast-changing markets.
Common Challenges and Considerations
While cloud computing offers many advantages, businesses should consider:
- Data governance and compliance
- Vendor dependency
- Network reliability
- Cost management
Understanding these factors helps organizations plan more effectively.
Secure cloud platforms also support plagiarism detection tools by protecting sensitive user data.
Best Practices for Using Cloud Services
To maximize value from cloud computing:
- Choose services based on actual needs
- Monitor usage and costs regularly
- Implement proper access controls
- Plan for data backup and recovery
These practices improve efficiency and reduce risks.
How Cloud Computing Services Support Modern Digital Systems
Postmodem Cloud computing is the platform for safe digital operation in both postmodem terrestrial social and enterprise networks of systems. From everyday applications to mission-critical enterprise infrastructure, cloud technology offers key advantages for organisations of all sizes. It’s conducive to growth, flexibility and productivity. Companies can implement successful systems by learning about cloud computing, with examples of real-world applications and architecture. As technology evolves, cloud computing will be a primary enabler of innovation in all sectors.
FAQs About Cloud Computing Services
Most cloud platforms use advanced security measures, but proper configuration and access control are essential for safety.
Yes, cloud computing services are ideal for small businesses because they offer low upfront costs while also providing the flexibility to scale as needs grow.
Common applications include data storage, web hosting, collaboration tools, analytics, and enterprise systems.
Virtualization is a means to maximize your hardware. It enables you to manage your virtual environments on a single machine.
